A New Standard for the Diagnosis of Sepsis Patients
Rapid Pathogen Identification Directly from Whole Blood,
Utilizing Revolutionary Single Molecule And Rapid
Tethering (SMART) Technology



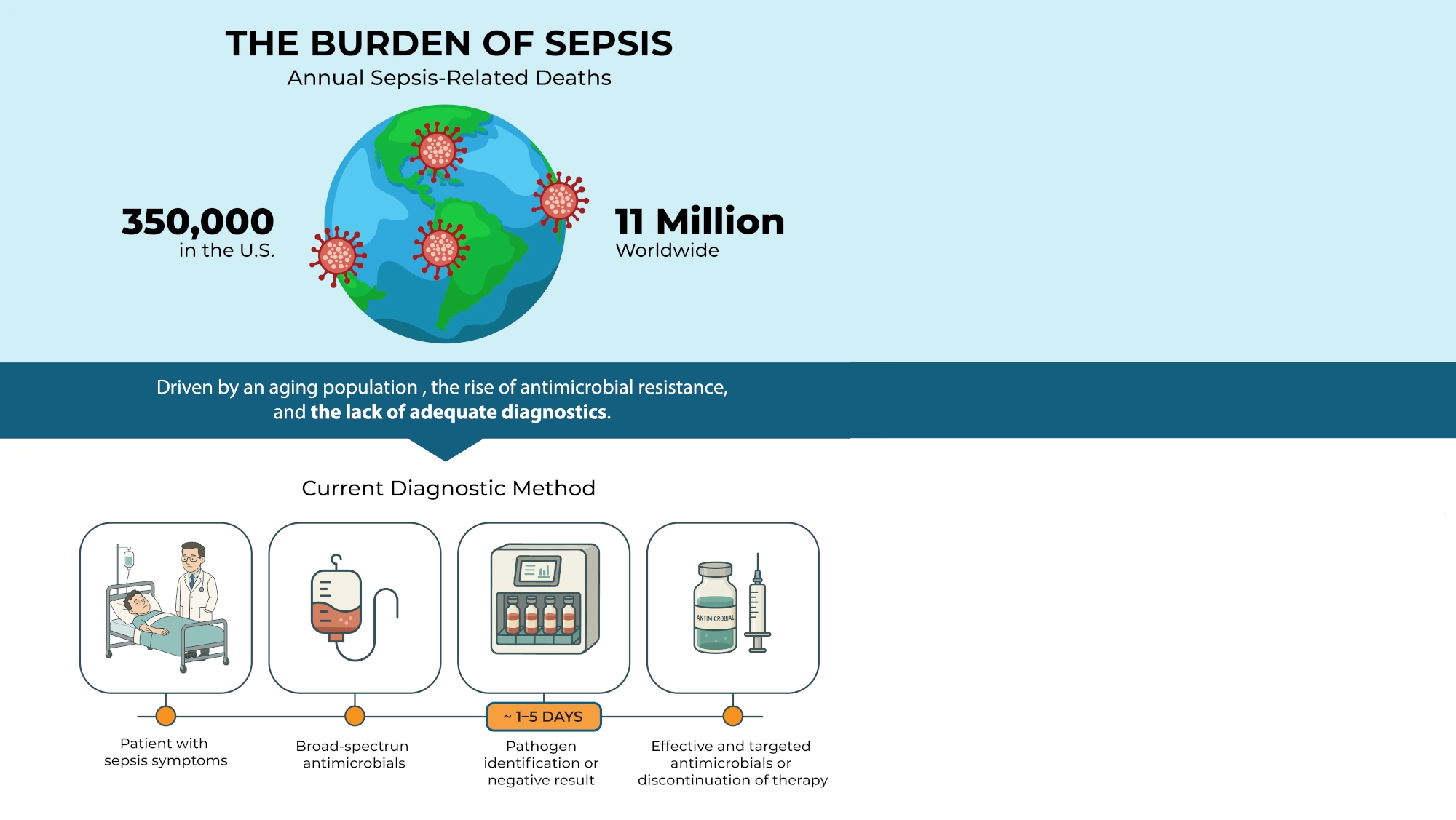
More than 1.7 million adults in the U.S. develop sepsis each year,
resulting in over 350,000 deaths. Globally, there are 50 million cases of sepsis every year and 11 million sepsis-related deaths.
Sepsis is the most expensive condition treated in U.S. hospitals. The annual aggregate hospital cost
for sepsis-related inpatient stays in the U.S. is over $50 billion.
Patients with sepsis require rapid and targeted antimicrobial treatment, but current diagnostic methods depend on blood cultures — a process that typically takes one or more days. This delay forces clinicians to administer broad-spectrum antimicrobials, which are often ineffective, excessively broad, or entirely unnecessary — potentially worsening patient outcomes and contributing to antimicrobial resistance.
Next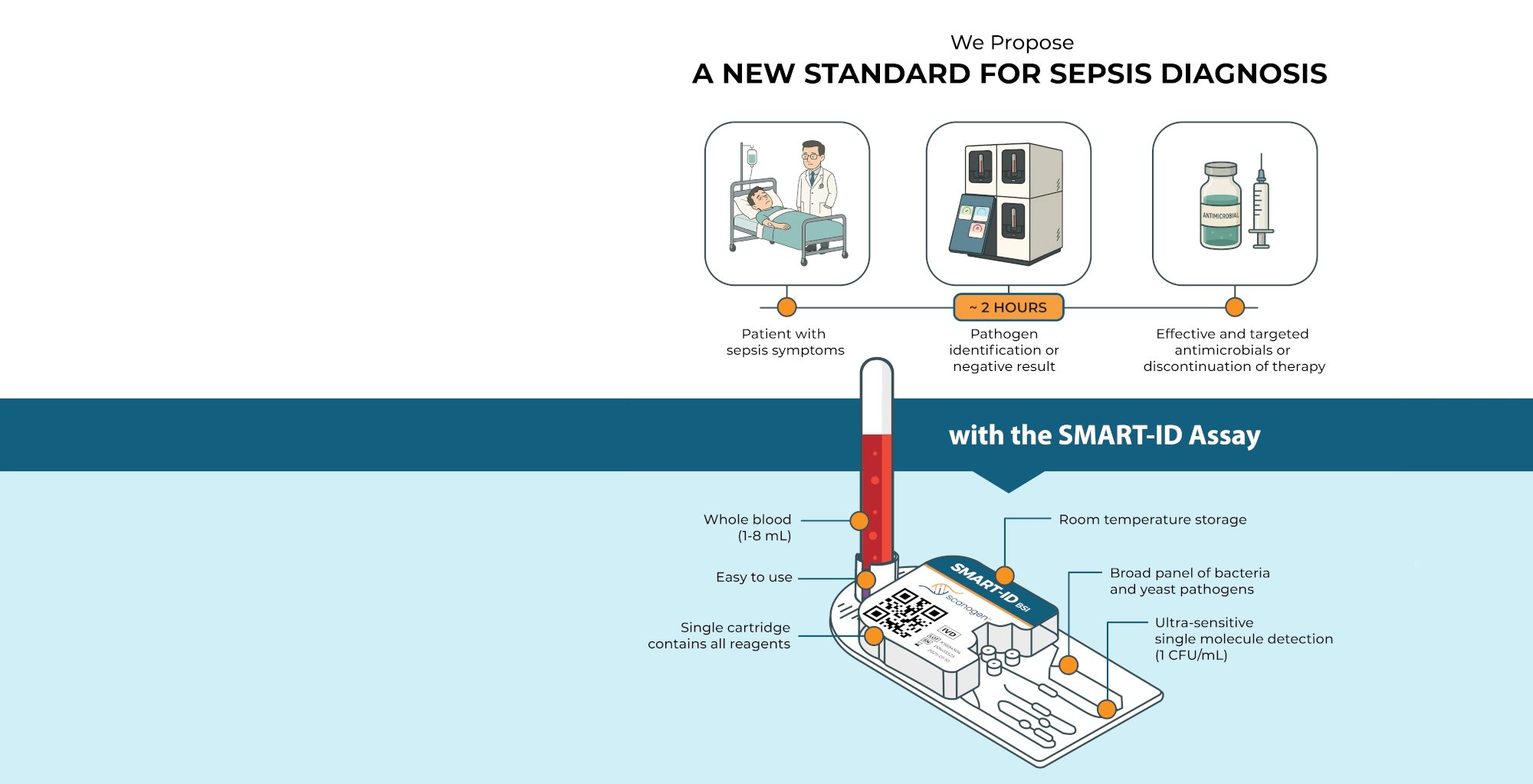
The SMART-ID assay analyzes whole blood to identify the pathogens that cause 95% of bloodstream infection cases within two hours. We believe that this accelerated diagnostic capability will dramatically enhance the management of patients suspected of sepsis. With timely pathogen identification, physicians can quickly initiate targeted antimicrobial therapy.

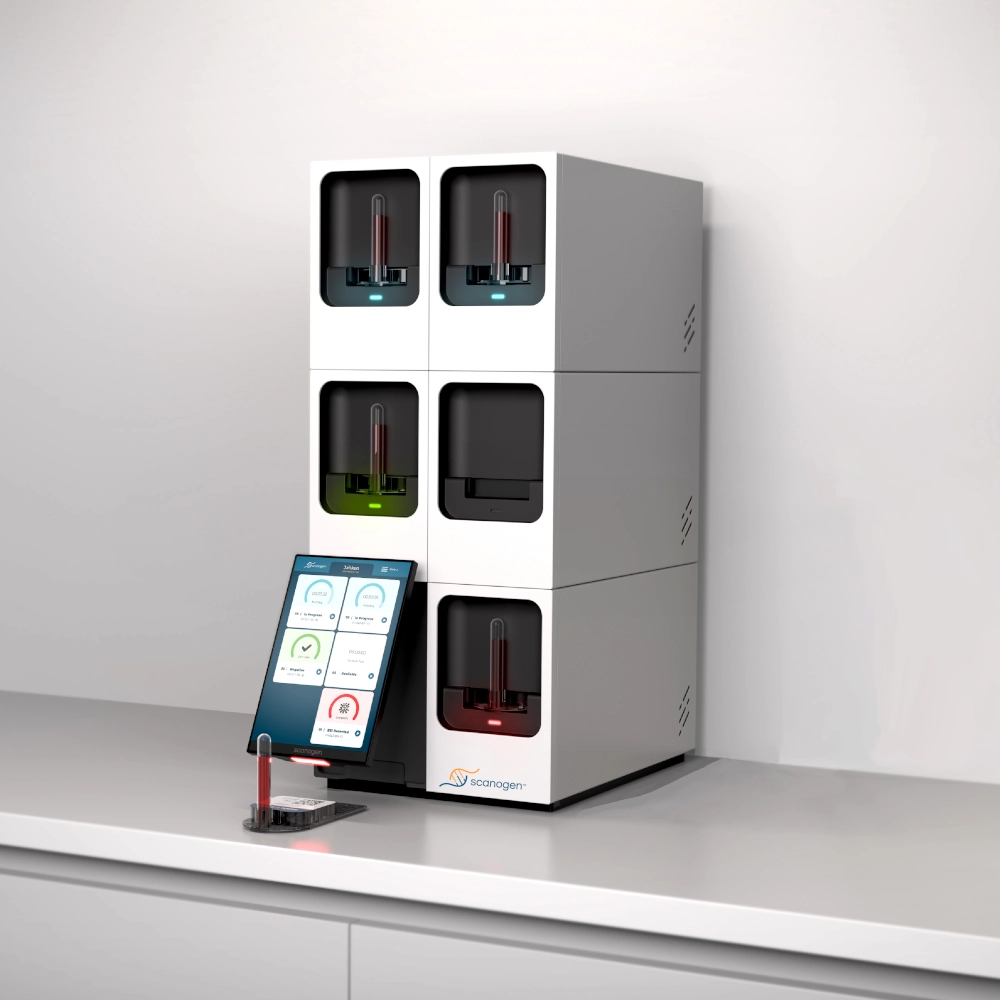
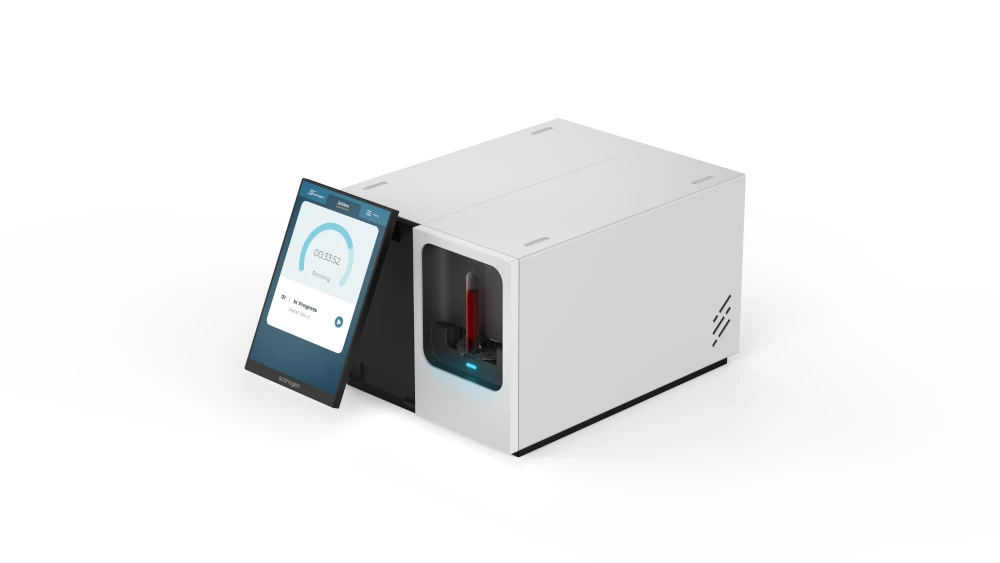
The S1 Instrument delivers SMART
molecular technology where results matter most—near the
patient.
Designed for point-of-care and near-patient settings, the S1 Instrument is ideal for use in
emergency departments, hospital wards,
STAT labs, and microbiology laboratories. Its compact, modular design offers unmatched
flexibility to meet the unique
throughput and spatial constraints of each environment.
Key Features:

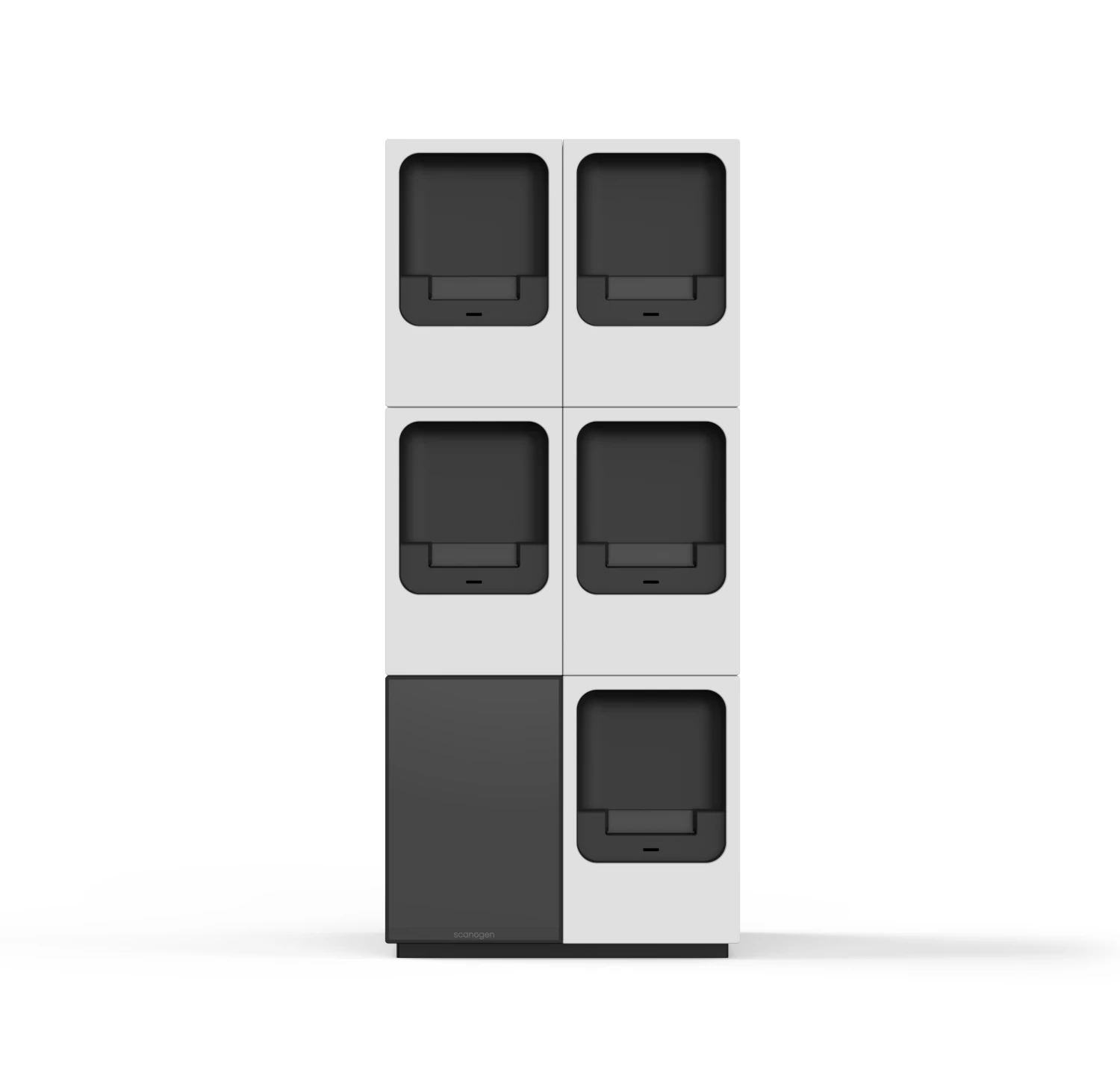
The S1 base configuration includes a touchscreen, barcode scanner, control unit, and one processing module capable of running a single test cartridge. The integrated touchscreen offers a streamlined interface for initiating tests and reviewing results. Additional modules can be easily stacked on top of the base unit, enabling users to expand or replace modules as needed—ensuring adaptability to changing testing volumes and workflows. The system supports integration with Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) to enable seamless data transfer and result reporting.
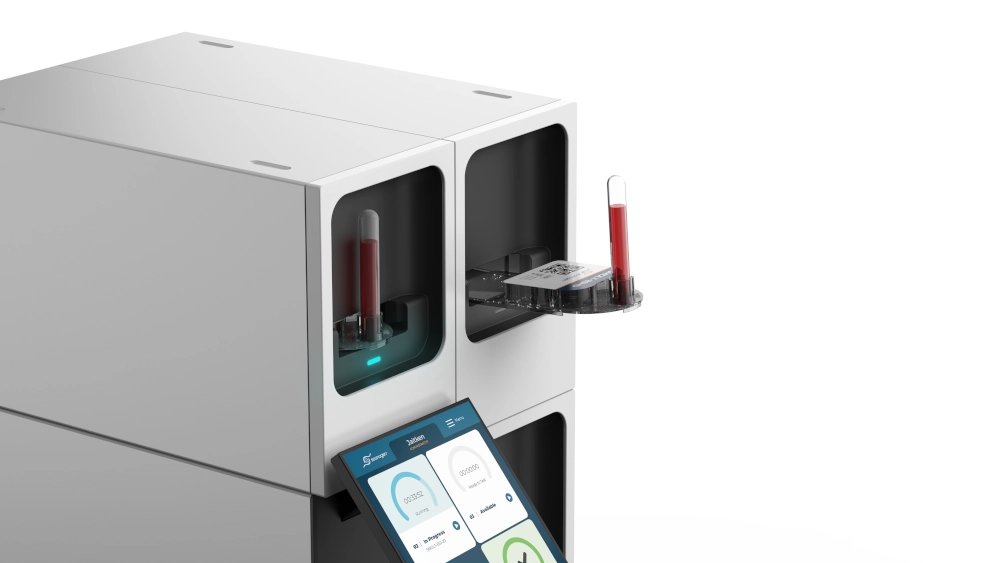

To initiate a test, the user simply scans and inserts a vacutainer into a test cartridge. The cartridge is then loaded into an available module within the instrument. From there, the module automatically processes the sample and generates a result, which is displayed on the instrument's touchscreen for immediate review.





